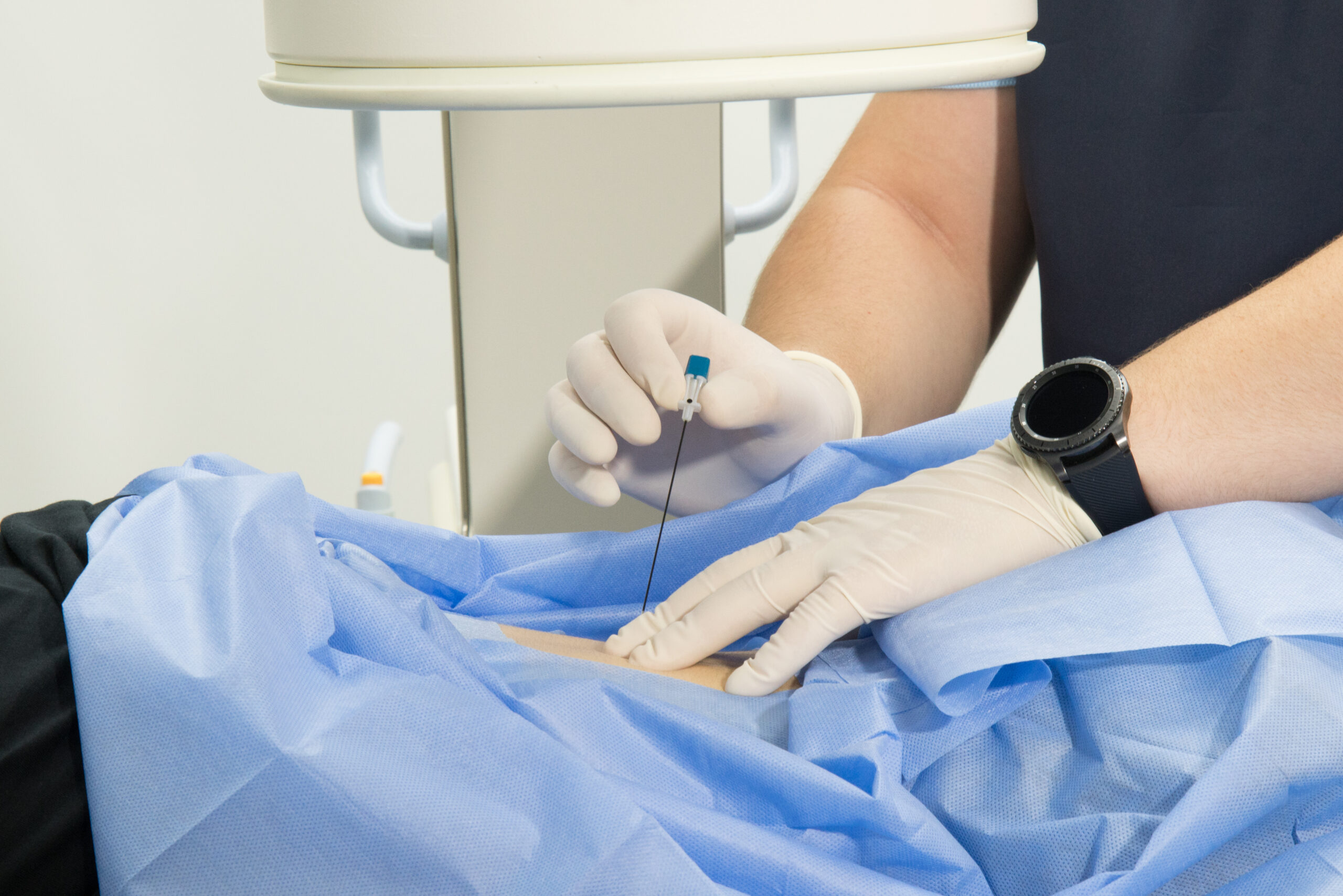
Sympathetic nerve blocks represent a significant advancement in the field of pain management, offering patients respite from chronic pain emanating from various conditions. They involve the administration of an anesthetic agent near the sympathetic nerves, a network of nerves spreading out from the spinal cord, orchestrating involuntary bodily functions. These blocks are instrumental in diagnosing and treating pain arising from the sympathetic nervous system.
The sympathetic nervous system, part of the autonomic nervous system, is crucial in controlling involuntary body functions, including blood flow and digestion. It prepares the body to respond to stress, initiating the ‘fight or flight’ response. However, in some instances, this system may play a role in propagating pain signals, leading to persistent pain even after the initial injury has healed.
Sympathetic nerve blocks are thus employed to interrupt these pain signals. In this procedure, an anesthetic is injected near the spine, targeting the specific nerve associated with pain. The relief experienced helps in diagnosing the role of sympathetic nerves in the pain pathway and provides therapeutic relief. It is commonly utilized for conditions like Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), a chronic pain condition affecting limbs, characterized by prolonged or excessive pain, changes in skin color, temperature, and swelling.
The efficacy of sympathetic nerve blocks is determined through meticulous patient assessment and precise identification of the sympathetic nerve implicated in the pain process. The use of imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound, aids in enhancing the accuracy of needle placement, minimizing risks, and enhancing the efficacy of the intervention.
However, like any medical procedure, sympathetic nerve blocks are not without risks and limitations. Potential complications include infection, bleeding, and allergic reactions to the anesthetic agents used. Moreover, the relief from pain is often temporary, necessitating multiple sessions or adjunctive treatments for prolonged benefits. A holistic approach, integrating physical therapy and psychological support, can augment the effectiveness of sympathetic nerve blocks, addressing not just the physiological but also the psychosocial aspects of chronic pain.
Additionally, research continues to unravel the intricacies of sympathetic nerve blocks. Scientists and clinicians are exploring novel anesthetic agents and techniques to extend the duration of pain relief and minimize side effects. Integration of technological advancements in imaging and drug delivery is envisioned to make these blocks more precise, effective, and accessible.
In conclusion, sympathetic nerve blocks serve as a pivotal tool in the multifaceted approach to managing chronic pain. They offer both diagnostic clarity and therapeutic relief, especially for conditions where the sympathetic nervous system is implicated. While associated with certain risks and limitations, ongoing research and technological innovations continue to enhance their safety and efficacy profiles. For patients besieged by chronic pain, sympathetic nerve blocks offer not just physical respite but also psychological and emotional alleviation, fostering an enhanced quality of life.
It is important to remember that patient individuality plays a crucial role, and not every patient will respond to this treatment in the same way. As such, a personalized approach, tailored to the specific needs and responses of each patient, is fundamental in optimizing the outcomes of sympathetic nerve blocks in pain management. The future of this therapeutic modality lies in the amalgamation of technological, pharmacological, and clinical advancements, converging to provide a more comprehensive, effective, and patient-centered solution to chronic pain.