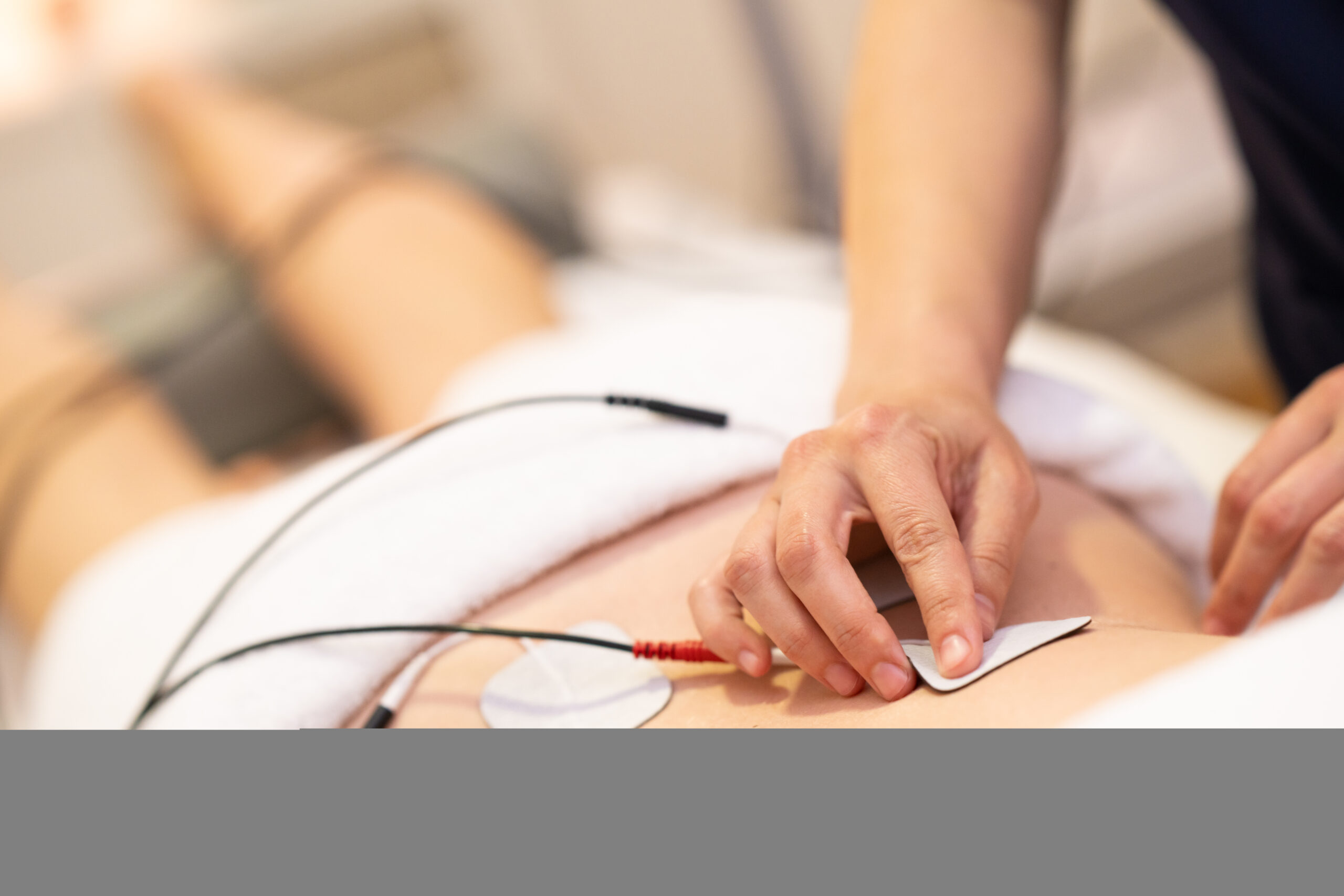
How Electrical Stimulation is Used to Treat Auto Injuries
Electrical stimulation, also known as electrotherapy, has emerged as a popular and effective treatment option for various auto injuries. The technique employs electrical currents to stimulate the nervous system, muscles, and soft tissues, promoting pain relief, muscle strength, and overall recovery. In this article, we’ll explore how electrical stimulation is used to treat auto injuries and its potential benefits.
Types of Electrical Stimulation
There are several types of electrical stimulation used in treating auto injuries, including Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), Interferential Current (IFC), and Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES). Each method targets specific issues and is applied according to individual patient needs.
TENS: TENS is a widely used method for pain relief, particularly in cases of whiplash, back pain, or neck pain. It works by sending low-voltage electrical pulses through the skin to stimulate nerve fibers and interfere with pain signals transmitted to the brain.
IFC: IFC employs alternating, medium-frequency currents to penetrate deeper into the tissues, providing relief from pain and inflammation. This method is particularly useful for joint injuries, muscle spasms, and edema caused by auto accidents.
NMES: NMES focuses on muscle rehabilitation and strengthening by delivering electrical impulses directly to the muscles. This treatment is particularly helpful in preventing muscle atrophy and improving range of motion in patients with limited mobility due to auto injuries.
Benefits of Electrical Stimulation
The use of electrical stimulation in treating auto injuries offers numerous benefits:
Pain Relief: Electrical stimulation works to block pain signals, providing immediate relief for many patients. It can also promote the release of endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers.
Reduced Inflammation: By stimulating the affected area, electrical stimulation can help decrease inflammation, reducing pain and promoting faster healing.
Muscle Strengthening: NMES aids in muscle recovery and strengthening, preventing muscle atrophy and helping patients regain mobility.
Increased Blood Flow: Electrical stimulation can improve blood flow to the affected area, which in turn speeds up the healing process by delivering essential nutrients and oxygen.
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free: Electrical stimulation is a non-invasive and drug-free treatment option, making it suitable for patients who may not respond well to medications or those who prefer to avoid invasive procedures.