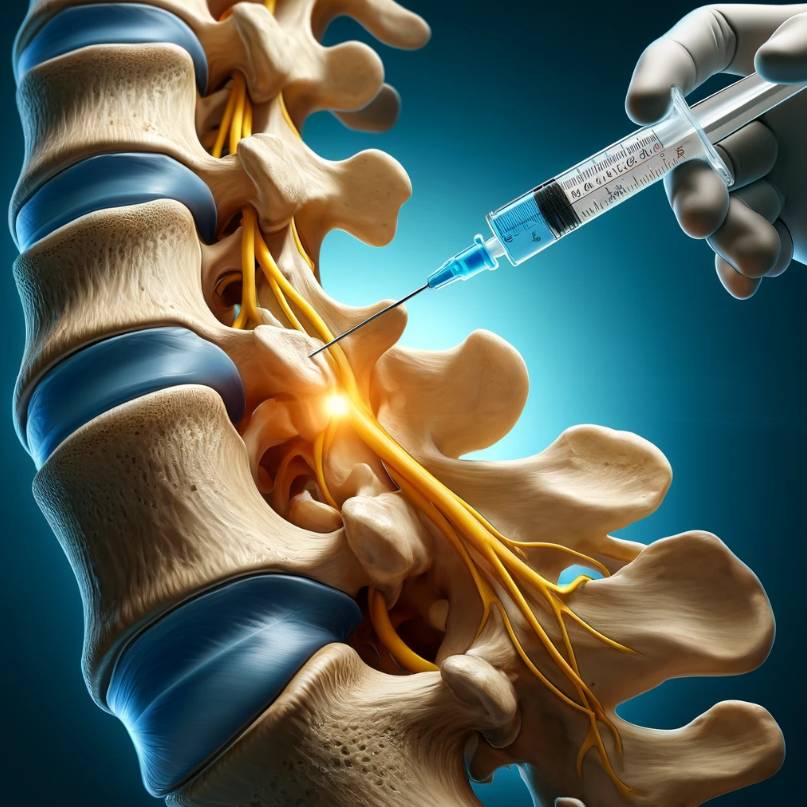
Medial branch blocks are a valuable diagnostic and therapeutic tool used in pain management to identify and alleviate pain originating from the facet joints of the spine. Facet joints, located on either side of the vertebrae, can become a source of chronic pain due to conditions such as arthritis, injury, or degenerative changes. Medial branch blocks target the medial branches of the spinal nerves that innervate these facet joints, offering both diagnostic insight and targeted pain relief for patients suffering from facet joint-related pain 1.
The procedure for performing a medial branch block involves the precise injection of local anesthetic medication near the medial branches of the spinal nerves that supply the affected facet joint. Prior to the injection, the patient may receive local anesthesia to numb the skin and underlying tissues, ensuring their comfort during the procedure. Under fluoroscopic guidance, a needle is advanced to the targeted medial branch, and a small amount of local anesthetic medication is injected to block the transmission of pain signals from the facet joint to the brain 2.
One of the primary uses of medial branch blocks is diagnostic. By temporarily blocking the medial branches responsible for transmitting pain signals from the facet joints, they help pain specialists confirm or rule out facet joint involvement as the source of a patient’s pain. This diagnostic information is valuable given the variety of conditions that can cause chronic back pain. If the medial branch block provides significant pain relief, it suggests that the facet joint is contributing to the patient’s symptoms, warranting further consideration for targeted treatment interventions 3,4.
Medial branch blocks can also serve as a therapeutic intervention for patients experiencing facet joint-related pain. While the duration of pain relief following a medial branch block varies from patient to patient, it can range from hours to weeks, providing a valuable window of opportunity for other treatments, such as physical therapy or minimally invasive interventions, to be initiated and optimized 1,5.
It is important to note that while medial branch blocks can be effective in providing short-term pain relief, they are not intended as a standalone or long-term solution for chronic pain management. Instead, medial branch blocks are often used as part of a comprehensive, multimodal approach to pain management, which may include medications, physical therapy, interventional procedures, and other modalities tailored to the individual patient’s needs 6,7.
Like any medical procedure, medial branch blocks carry potential risks and complications, including infection, bleeding, nerve injury, and allergic reactions to the medications used 1,8. However, when performed by experienced and skilled practitioners in a controlled clinical setting, medial branch blocks are generally safe and well-tolerated by patients.
In conclusion, medial branch blocks are a valuable tool in the field of pain management, offering both diagnostic insight and targeted pain relief for patients with facet joint-related pain. By selectively blocking the transmission of pain signals from the facet joints to the brain, medial branch blocks help pain specialists identify the source of a patient’s pain and provide temporary relief to improve their quality of life.
References
1. Royal Orthopaedic Hospital – Medial Branch Block. Available at: https://roh.nhs.uk/services-information/pain-management/medial-branch-block. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)
2. Medial Branch Injection Procedure | Spine-health. Available at: https://www.spine-health.com/treatment/injections/medial-branch-injection-procedure. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)
3. Medial Branch Block | Pain Management. Available at: https://intermountainhealthcare.org/services/pain-management/treatments-and-procedures/procedures/medial-branch-block/. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)
4. Medial Branch Nerve Blocks | Spine-health. Available at: https://www.spine-health.com/treatment/injections/medial-branch-nerve-blocks. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)
5. Liu, M., Shaparin, N., Nair, S., Kim, R. S. & Hascalovici, J. R. Chronic low back pain: The therapeutic benefits of diagnostic medial branch nerve blocks. Pain Physician (2021). doi:10.36076/ppj.2021.24.e521
6. Understanding Medial Branch Blocks | Commonwealth Spine & Pain. Available at: https://commonwealthspineandpain.com/understanding-medial-branch-blocks/. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)
7. Bartleson, J. D. & Maus, T. P. Diagnostic and therapeutic spinal interventions: Facet joint interventions. Neurol. Clin. Pract. (2014). doi:10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000044
8. Facet and Medial Branch Blocks for Pain – Brigham and Women’s Hospital. Available at: https://www.brighamandwomens.org/anesthesiology-and-pain-medicine/pain-management-center/facet-and-medial-branch-blocks. (Accessed: 28th April 2024)